In Saudi Aramco, SABIC and other big oil and gas companies, where safety rules are very strict, being a Fire Watcher is a very important job. A Fire Watcher needs to stay alert, spot dangers before they become problems, and act quickly in any emergency. Knowing what kinds of questions employers ask can help you feel more confident and do better in a Fire Watcher Interview. We put together a list of the most important Fire Watcher interview questions that are often asked in Saudi Aramco, SABIC, and international projects. This will help you get ready and show that you are a strong candidate.
Fire Watcher Interview Questions
1. What is fire?
Fire is a chemical reaction between Fuel, Oxygen and Heat. It produce Heat, Light, and Smoke.
2. What are the elements of Fire?
There are four elements of fire:
- Fuel (something that can burn)
- Oxygen (from the air)
- Heat (enough to start the burning)
- Chemical Chain Reaction (the process that keeps the fire going)
These elements are also known as the Fire Tetrahedron. If you remove any one of these, the fire will stop.
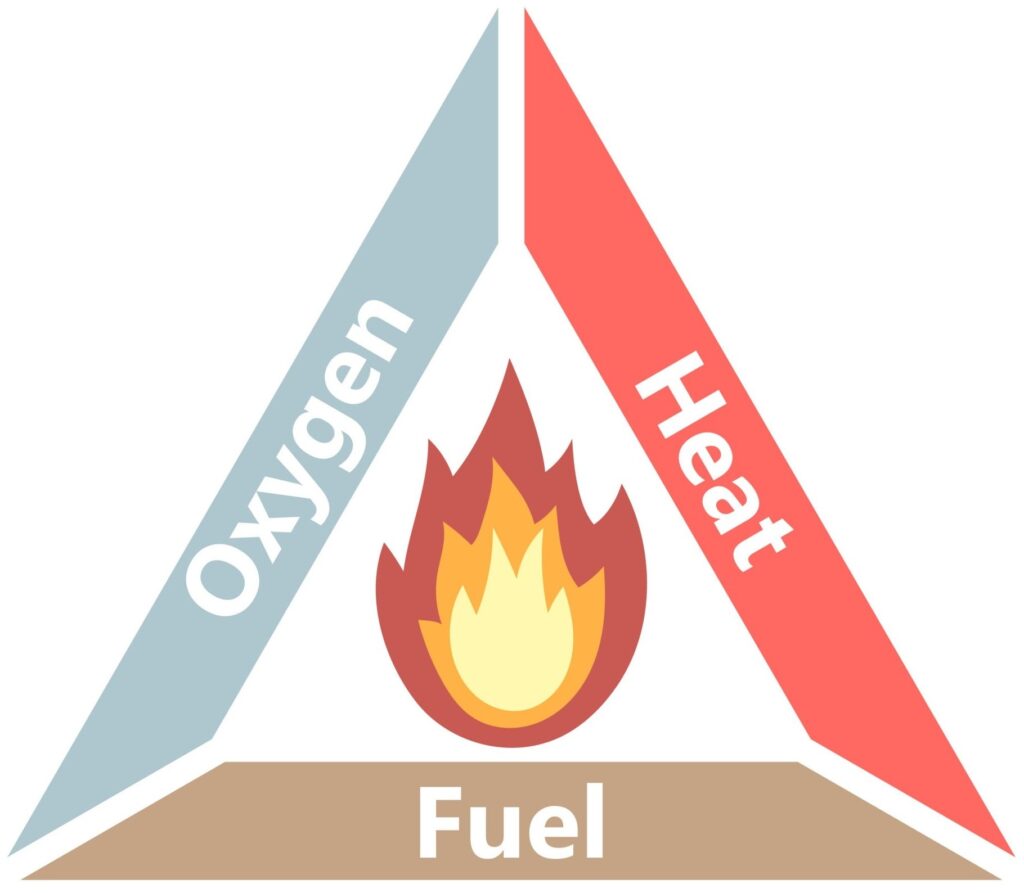
3. What is fire triangle?
The fire triangle is a diagram that shows the three basic elements needed for fire: Oxygen, Heat, and Fuel. If any one of these is removed, the fire will stop.
4. What are the Classification of fire?
Indian Standard (IS 15683 : 2018)
| Class A | Ordinary Solid Material Fires | Example : Wood, Paper & Clothes |
| Class B | Flammable Liquid Fires | Example : Diesel, Petrol & Paints |
| Class C | Flammable Gases Fires | Example : Hydrogen, Acetylene, LPG |
| Class D | Combustible Metal Fires | Example : Sodium, Potassium, Aluminum |
| Class F | Cooking Oil Fires / Kitchen Fires | Example : Vegetable Oils and Fat |
British Standard BS EN 2 (UK, EU)
| Class A | Ordinary Solid Material Fires | Example : Wood, Paper, Rubber |
| Class B | Flammable Liquid Fires | Example : Diesel, Petrol, Alcohol |
| Class C | Flammable Gas Fires | Example : Hydrogen, Acetylene |
| Class D | Combustible Metal Fires | Example : Sodium, Potassium |
| Class F | Cooking Oil Fires / Kitchen Fires | Example : Vegetable oils and fat |
BS EN does not have Class E. Electrical fires are not a separate class. They are handled using the other classes (A to F) depending on the material burning.
| Class A | Ordinary Combustibles Material Fires | Example : Wood, Paper, Clothes, Trash |
| Class B | Flammable Liquid & Gases | Example : Diesel, Petrol, Gasoline, Oil |
| Class C | Energized Electrical Equipment Fire | Example : Live Wires, Motors, Short Circuits |
| Class D | Combustible Metal Fires | Example : Sodium, Potassium |
| Class K | Cooking Oil Fires / Kitchen Fires | Example : Vegetable oils and fat |
In the NFPA system, there is a Class K fire, which is equal to Class F in the BS/IS standards.
5. What are the main types of fire extinguisher?
- Water
- Foam
- Dry Chemical Powder (DCP)
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂)
- Wet Chemicals
6. What are the colour codes of Fire extinguisher?
- Water – Red
- Foam – Cream
- Dry Chemical Powder (DCP) – Blue
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) – Black
- Wet Chemical – Yellow
7. Colour Codes of Fire Extinguisher and where is it used?
| Extinguisher Type | Color Code | Where is it used? |
|---|---|---|
| Water | Red | Wood, Paper (Class A) |
| Foam | Cream | Oil, Petrol (Class B) |
| Dry Chemical Powder (DCP) | Blue | Multipurpose (A, B, C) |
| Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) | Black | Electrical Fires |
| Wet Chemical | Yellow | Kitchen Cooking Oil (Class K) |
8. What is fire extinguishing principle?
The fire extinguishing principle means stopping the fire by removing one or more elements of the fire triangle.
9. What are the types of fire extinguishment methods?
The main fire extinguishment methods are:
- Cooling: Removing heat (usually done with water).
- Starvation: Removing or cutting off the fuel.
- Smothering: Removing oxygen or covering the fire.
- Chain Breaking: Stopping the chemical chain reaction (Done by DCP or Blanketing).
10. What are the methods for fire can spread?
Fire spreads through the transfer of heat. The three main methods of heat transfer that cause fire to spread are:
- Conduction: Heat travels through a solid material.
Example: A metal pipe passing through a wall can carry heat from a fire in one room and ignite combustible materials in the next room. - Convection: Heat is carried by moving air or liquids.
Example: Hot gases and smoke from a fire rise, heating up the upper floors of a building and causing the fire to spread upwards. - Radiation: Heat travels in straight lines as invisible waves, like the heat from the sun.
Example: The intense heat from a large fire can radiate across a street, igniting nearby buildings without direct contact.
11. What is PASS rule?
- P – Pull the pin
- A – Aim at the base of the fire
- S – Squeeze the Trigger
- S – Sweep side to side
12. What are the precautions for welding?
- Remove all combustible materials from the welding area.
- Clear the work area and cover wooden floors with a fireproof blanket.
- Set up a fire blanket booth around the welding spot.
- Ensure the welding machine is properly earthed (double earthing).
- Keep the welding area dry and free from water.
- Keep fire extinguishers or sand buckets nearby.
- Barricade the work area and display warning signboards.
- Use required PPE such as leather gloves, goggles, and welding helmets.
- Switch off the power when welding is not in use.
13. Which fire extinguisher should be used on a trash bin full of paper ignited by a cigarette?
Class A – A fire extinguishers are used on ordinary combustible materials
Example: Water Type Fire Extinguisher
14. What is flash point?
Flash point of a particular material is the lowest temperature at which vapour of the material undergoes ignition in the presence of an ignition source. Flash point produce only flash in the present of ignition source. The flash point of a liquid can change if the surrounding air pressure changes.
- Example: Diesel (52 to 96 Degree Celsius)
15. Define Auto Ignition Temperature?
Auto ignition temperature is the lowest temperature at which a substance will ignite on its own in normal air, without any external ignition source like a flame or spark.
16. What is fire point?
The fire point is the lowest temperature at which the vapors of a substance keep burning even after the ignition source is removed. At this temperature, the fire continues on its own. Flash point is always less than the fire point
- Example: Diesel (120 Degrees Celsius)
17. What advice would you give the CEO of fire watch about how to improve it?
Improve fire watch by keeping the workplace free of combustible materials, covering unsafe areas with fire blankets, and ensuring all workers understand the hazards.
18. What is hot work?
Hot work is any activity that produces heat, flames or sparks such as welding, cutting, grinding, soldering, brazing or melting metals and other materials.
19. What PPE is required for hot work?
Proper PPE must be worn during any hot work. At minimum, eye, face, and hand protection are required.
Fire watch attendants must also wear suitable PPE.
Additional PPE like safety boots, gloves, hard hat, fall protection, and flame-resistant clothing should be used as needed according to OSHA requirements.
20. Who issues hot work permit?
A Hot Work Permit is issued by a designated and authorized person known as a “Permit Authorizing Officer” (PAO) or simply the “Permit Issuer.”
21. What is LEL & LEL ?
- Lower Explosive Limit (LEL) – The lowest concentration of a gas or vapor in air that can burn or explode if an ignition source is present.
- Upper Explosive Limit (UEL) – The highest concentration of a gas or vapor in air that can burn or explode if an ignition source is present.
- Between LEL and UEL: The gas mixture is explosive.
- Below LEL: The mixture is too lean to burn.
- Above UEL: The mixture is too rich to burn.
| Gas | LEL | UEL |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 4 | 75 |
| Hydrogen Cyanide | 5.6 | 40 |
| Hydrogen Sulfide | 4 | 44 |
| Isobutane | 1.8 | 8.4 |
22. Who is fire watcher?
A Fire Watcher is a trained and competent person assigned to monitor the area during and after hot work activities. Their primary duty is to be fully focused on safety watching for sparks, heat, or any signs of fire.
23. What are the main jobs of a fire watcher?
The main job of a fire watcher is to monitor the hot work area and raise the alarm immediately if a fire starts. They may try to control a small fire, but their primary role is not to fight the fire their main duty is to alert emergency responders so they can handle it safely.
24. What are the responsibilities of Fire watcher?
- Watch for any hazardous conditions and stop the hot work if a fire risk appears.
- Keep fire extinguishing equipment nearby and know how to use it properly.
- Be familiar with alarm systems and know how to notify emergency services.
- Follow all conditions written on the hot work permit.
- Inspect the work area for flammable vapors or liquids before, during, and after the job.
- Ensure fireproof shields, covers, and blankets remain in place.
- Never leave the hot work area while the job is ongoing.
- Stay on duty, even during breaks, until 30 minutes after the hot work is completed.

